What is Risk Register for Finance Leaders

What Is a Risk Register and Why Does It Matter for Finance Leaders?
A risk register is a key tool for finance leaders looking to identify, track, and mitigate potential threats to their organization. By organizing risks by category and severity, finance professionals can proactively address vulnerabilities before they lead to financial losses. Whether the risk is financial, operational, strategic, or regulatory, a well-maintained risk register empowers CFOs to make informed, forward-looking decisions and allocate resources where they’re needed most.
As a finance leader, it is crucial to have the right tools in your arsenal to ensure successful outcomes and mitigate risks. One way to do this is by utilizing a risk register. A risk register is a document that contains an organized list of all the risks facing your business, along with information about their impact on the organization. By understanding what risks you face, you can create plans to mitigate them and minimize their effects. In this blog, we will explore the importance of a risk register for the finance industry, the types of risks that are typically included, and how finance leaders can use them to make informed decisions.
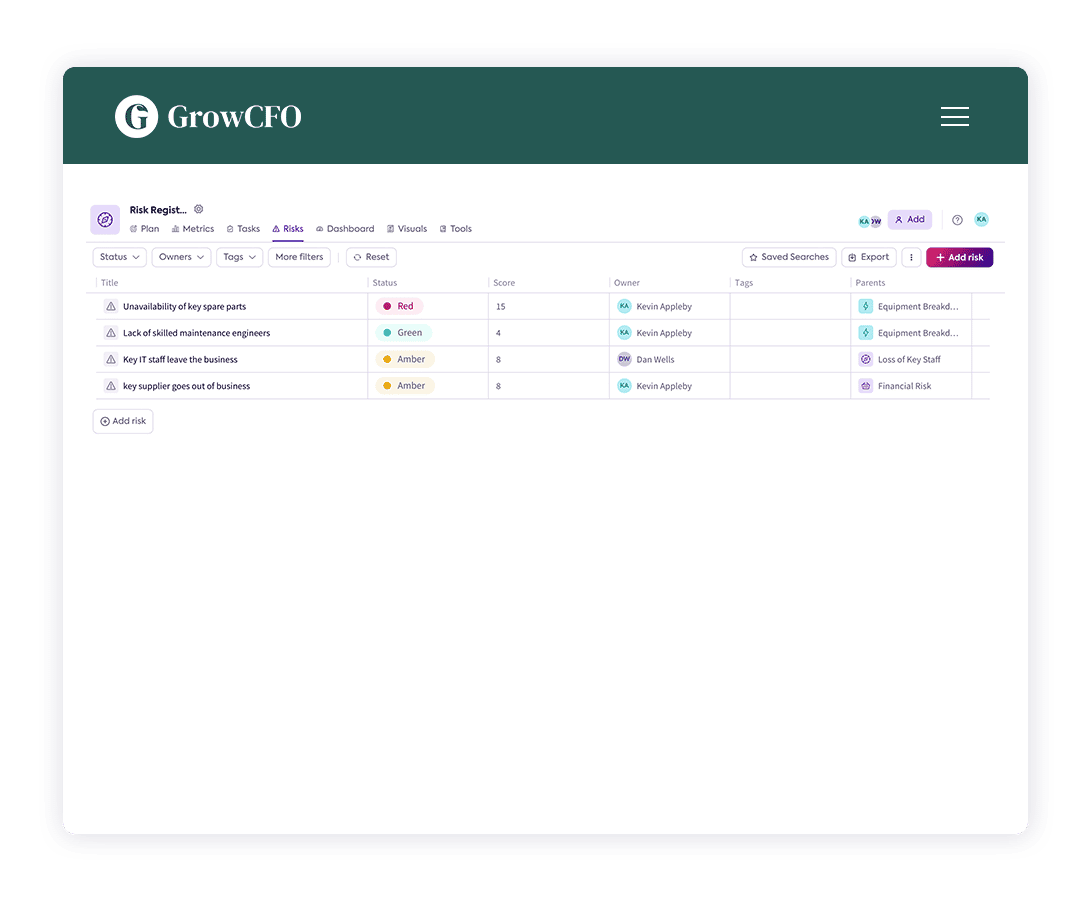
What Is a Risk Register — and How Does It Work?
The finance industry is constantly evolving and facing new challenges, from economic fluctuations to technological advancements. As a result, finance leaders must be vigilant in identifying and managing potential risks that could impact their organization. A risk register is a tool that helps finance leaders do just that.
A risk register is a document that lists all the potential risks that an organization may face, along with an assessment of the likelihood and impact of each risk. It is a comprehensive document that includes all types of risks, including financial, operational, strategic, and compliance risks. By identifying these risks and their potential impact, finance leaders can take proactive measures to mitigate or manage them, thus minimizing the potential negative impact on the organization.
What Types of Risks Should Finance Leaders Include in a Risk Register?
Financial Risk
One of the most important types of risks that finance leaders must consider is financial risk. Financial risks include market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk. Market risk refers to the potential impact of market fluctuations on an organization’s financial performance. Credit risk is the risk of loss due to a borrower’s inability to repay a loan. Liquidity risk is the risk of an organization not being able to meet its financial obligations as they come due. By identifying these risks and their potential impact, finance leaders can take steps to mitigate or manage them, such as diversifying investments or implementing stricter lending standards.
Operational Risk
Operational risks are another type of risk that finance leaders must consider. These risks include the risk of a natural disaster, cyber attack, or other operational disruptions that could impact an organization’s ability to function. By identifying these risks and their potential impact, finance leaders can take steps to mitigate or manage them, such as implementing disaster recovery plans or enhancing cybersecurity measures.
Strategic Risk
Strategic risks are also important for finance leaders to consider. These risks include the risk of a merger or acquisition not being successful or a new product or service not being well received. By identifying these risks and their potential impact, finance leaders can take steps to mitigate or manage them, such as conducting thorough due diligence before making a merger or acquisition or conducting market research before launching a new product or service.
Compliance Risk
Compliance risks are also an important consideration for finance leaders. These risks include the risk of non-compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards. By identifying these risks and their potential impact, finance leaders can take steps to mitigate or manage them, such as implementing compliance programs or conducting regular audits.
How Can Risk Registers Benefit Finance Leaders?
Risk registers are especially beneficial for finance leaders because they provide insight into areas where there may be hidden financial risks that could have significant impacts on their organizations’ bottom line if not properly addressed. By having visibility into these areas, CFOs can better understand and anticipate potential financial losses before they occur so they can take steps to reduce or eliminate them altogether. Additionally, having a clear picture of all the risks facing their organizations gives finance leaders greater control over which ones should be prioritized based on their relative likelihood and severity so that resources can be allocated accordingly.
For example, let’s say that a finance leader discovers through their risk register that one of their top suppliers has recently had some financial difficulties due to an unexpected downturn in demand for their product. With this information readily available in the risk register, they can quickly adjust plans accordingly by arranging alternate sources of supply or re-evaluating existing contracts in order to ensure continuity of operations while minimizing any potential financial losses caused by the supplier’s instability. This allows CFOs and other finance leaders to make more effective decisions when it comes to managing organizational finances as well as anticipating future conditions within their markets and industries.
Conclusion
Risk registers provide invaluable insight into potential risks facing organizations so CFOs and other finance leaders can make informed decisions about how best to mitigate those risks while protecting against potential losses. Having visibility into these areas allows CFOs to better anticipate market conditions ahead of time so they can develop strategies for addressing them proactively rather than reacting after-the-fact when damages have already been done. Ultimately, having an up-to-date risk register gives finance leaders greater control over how resources are allocated throughout their organizations while providing valuable insights into areas where there may be hidden financial vulnerabilities that need attention before disaster strikes. Thus, making this tool essential for finance professionals seeking success in today’s competitive landscape!







Responses